GTY 609: Qualitative Research Methods: Methodical Searching
Methodical Searching
Searching methodically means
- Your research is open and easier to repeat
- Helps to make sure no relevant resources of missed
- Keeps you from repeating yourself
- Helps keep your research organized
Keeping Track
Advanced Searches in Databases
AND, OR & NOT
Field Searches
Proximity Searches
Nesting
Truncation and Wildcard
Finding Similar Articles with Google Scholar
Keeping Track
Find a method that works with you to keep track. You can try this Search Log. It is divided into the three parts of methodical searching.
- Developing your search strategy
- Tracking your searches
- Tracking information about your resources
Advanced Searches in Databases
AND, OR & NOT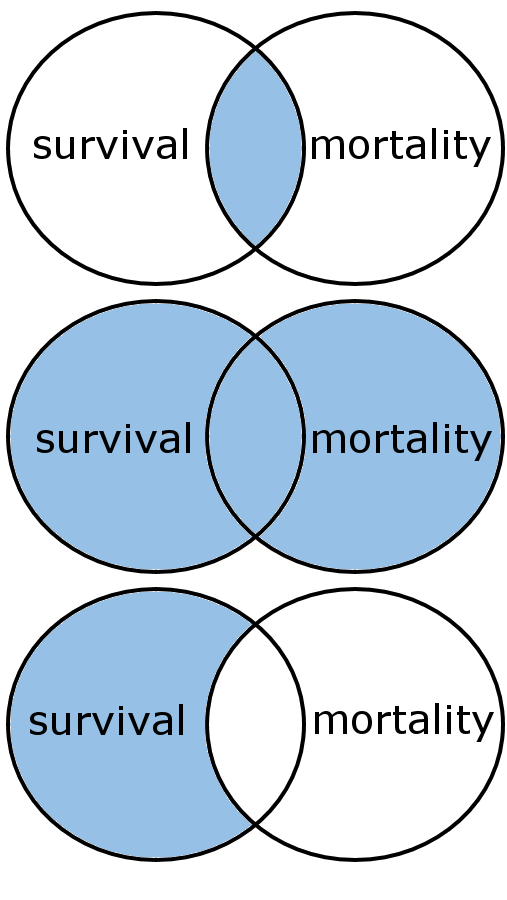
AND, both terms must be in the hits
OR, either terms can be in the hit (good for
synonyms)
NOT, removes hits with the not term (Google products use the minus (-) sign.)
Advanced Searches in Databases: Field Searches
Database searches search every field in the detailed record. You can some searches by field. Great ones to use are author, and subject headings. Here is a video on using subject headings in three different databases
Advanced Searches in Databases: Proximity Searches
As part of proximity searches, you can specify how close, and in what order, you want the search terms to appear. The proximity operators are usually composed of a letter (N) or word (NEAR) and a number (to specify the number of words appearing between your search terms). For EBSCOHost databases use the letter (N) and Google products use AROUND(#).


Advanced Searches in Databases: Truncation & Wildcards
Truncation and Wildcards are very database specific. Usually the star symbol (*) finds multiple variations, like gr*y finds both grey and gray. The question mark (?) typically is used for unknowns.
Advanced Searches in Databases: Nesting
Nesting also called Grouping keeps alike keywords together, and uses the OR within the parentheses and AND between. For example,
(older adults OR elderly OR geriatric OR geriatrics OR aging OR senior OR seniors OR older people OR aged 65 or 65+ AND (assisted living facilities OR assisted care facilities OR long term care OR nursing home)
Finding Similar Articles Using Google Scholar
Places to find similar articles are
Reference list of the article
'Similar Articles' in PubMed
'Cited by' in Google Scholar
1. Click on the 'Cited by' link in the last line of the entry.

2. If it is a large number, click box below title and use a simplified search to limit your results.

Finding Similar Articles Using Web of Science
You can find articles that a paper used as references and ones that have cited the article in Web of Science
1. Copy and paste the title into the search box. Use the down arrow to change the search option from all fields to 'Title'. Click the 'search' button.

2. On the right hand side of the article title will be two numbers. First is 'citations'. These are the articles that used your original article as a reference. Second is 'references'. These are the resources that your original article used as references. Click on the number for the list of the resources

3. You can use the limiters on the left hand side of the results list to narrow down your results.
